I. Introduction
Through the monitoring of mine geological environment, we will further understand the problems of mine geological environment and its hazards, master the dynamic changes of mine geological environment, predict the development trend of mine environment, rationally develop mineral resources, protect mine geological environment, carry out comprehensive improvement of mine environment, and mine ecological environment. Provide basic data and basis for restoration and reconstruction and implementation of mine geological environment supervision and management.
Second, the work task
(1) Carry out geological environment monitoring of individual mines and monitoring of geological environment of mines in regional concentrated mining areas or group mining sites;
(2) Establish a mine geological environment monitoring database and information system;
(3) Analysis, processing and sharing of mine geological environment monitoring data;
(4) Evaluation and prediction of mine geological environment quality;
(5) Proposing suggestions for mine geological environment management control measures and comprehensive countermeasures for mine geological environment;
(6) Prepare an annual report on mine geological environment monitoring;
(7) Providing information services on mine geological environment to the society.
Third, the workflow
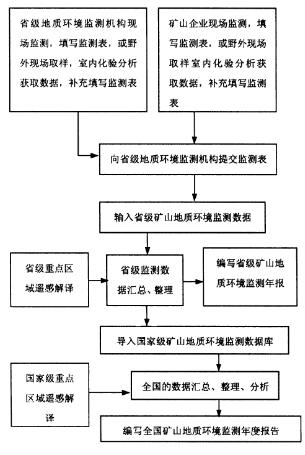
Fourth, monitoring indicators
(1) Encroachment, destruction of land and land reclamation monitoring: encroachment and destruction of land types and areas, destruction of land methods, destruction of vegetation types and areas, reclaiming and reclaimed land area.
(2) Solid waste and its comprehensive utilization monitoring: type of solid waste, annual discharge, accumulated stock, source, annual comprehensive utilization, main hidden dangers of solid waste pile, and land area occupied by pressure.
(3) Tailings pond monitoring: the number and scale of tailings ponds, the amount of tailings accepted in the year, the main harmful components of tailings, major hidden dangers, and annual comprehensive utilization.
(4) Monitoring of ground subsidence (collapse) in goaf: number of subsidence areas, collapse area, maximum depth of collapse pit, depth of water accumulation, degree of collapse and so on.
(5) Mountain cracking, landslide, collapse, and debris flow geological disaster monitoring: the number of occurrences in the current year, the hazards caused, the number of hidden danger points or hidden danger areas of geological disasters, and the number of hidden danger points or hidden danger areas that have been treated.
(6) Soil erosion and land desertification monitoring: area and treatment of soil erosion and land desertification.
(7) Surface water pollution monitoring in mining area: waste water type, annual output, annual discharge, annual treatment, discharge destination, surface water pollution source, main pollutants, pollution degree and damage caused, annual recycling, Annual throughput.
(8) Soil pollution monitoring: pollution sources of soil pollution, major pollutants, pollution levels and hazards.
(9) Ground crack monitoring: the number of ground fissures, the maximum crack length, width, depth, the direction of the ground fissure, and the degree of damage.
(10) Wastewater discharge monitoring: annual wastewater discharge and discharge standards, main hazardous materials and discharge destinations, annual wastewater treatment capacity and comprehensive utilization.
(11) Groundwater monitoring: 1 Groundwater balance damage monitoring: Groundwater level in mining area, annual drainage of mine pit, aquifer area of ​​groundwater, groundwater funnel area, etc.; 2 Groundwater quality pollution monitoring: pH, ammonia nitrogen, nitrate, nitrite, volatilization Phenolics, cyanide, arsenic, mercury, chromium (hexavalent), total hardness, lead, fluorine, cadmium, iron, manganese, total dissolved solids, permanganate index, sulfate, chloride, coliform And other projects that reflect major water quality problems in the region.
V. Monitoring methods
1. Monitoring method for a single mine
(1) Ground subsidence monitoring in goaf: If the mining area is large, it will be monitored by remote sensing technology; the key mining areas will be monitored by high-precision GPS, borehole inclinometer, total station, etc., and other artificial field surveys and measurements will be used.
(2) Ground crack monitoring in mining areas: The main monitoring methods include geodetic survey, GPS global positioning system, simple manual observation, and stress gauge.
(3) Monitoring of land subsidence in mining areas: Key mines are automatically monitored by site-buried bedrock standards, and others are monitored by high-precision GPS. The GPS monitoring method refers to the relevant specifications [7].
(4) Monitoring of mountain cracking in mining area: manual site survey and measurement are used.
(5) Monitoring of collapse, landslide and debris flow in mining areas.
(6) Soil and water loss monitoring in mining areas: the combination of remote sensing technology monitoring and manual site survey and measurement.
(7) Monitoring of land desertification in mining areas: dynamic monitoring of groundwater level and ground GPS monitoring and remote sensing satellite monitoring.
(8) Mining area invasion and destruction of land and land reclamation monitoring: manual site survey, measurement, supplemented by remote sensing technology.
(9) Soil pollution monitoring in mining areas: artificial site survey, sampling analysis, supplemented by soil pollution automatic monitor.
(10) Monitoring of surface water bodies in mining areas: artificial site survey, sampling analysis.
(11) Groundwater Equilibrium Destruction Monitoring in Mining Area: Artificial site survey, sampling analysis, supplemented by automatic groundwater level monitor.
(12) Wastewater discharge monitoring: manual site survey, sampling analysis.
(13) Groundwater quality monitoring: manual site survey, sampling analysis.
(14) Seawater intrusion monitoring: manual site survey, sampling analysis.
2. Regional monitoring methods
Multi-band, multi-temporal and high-resolution remote sensing images are used. Interpret and interpret the geological environment of the mine in the area. Based on remote sensing spectrum, the automatic identification models and methods of major mine land types, land and vegetation damage, ground subsidence, etc. with certain precision guarantees are established to realize automatic monitoring of ground area changes.
Sixth, system equipment
Mine geological environment monitoring system composition topology diagram
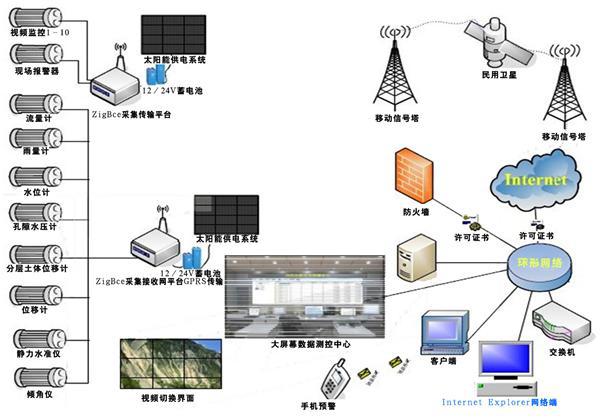
Function: 1. Groundwater level monitoring 2. Surface water level monitoring 3. Monitoring of groundwater pressure 4. Surface water flow monitoring 5. Regional rainfall monitoring 6. Regional meteorological environmental monitoring 7. Geological soil settlement monitoring 8. Horizontal displacement monitoring of geological soil layers 9 , geological crack monitoring and cracking 10, building settlement monitoring 11, building tilt monitoring 12, key area on-site safety video monitoring 13, residential area online hearing monitoring tips
Wholesale custom stainless steel coffee filter paper holder V shape coffee filter paper stand
Coffee Filter Holder, Handmade Coffee Filter Holder Coffee Paper Storage Rack Filter Paper Base Bracket Container Stand
Barista Tools Stainless Steel Hand Drip V-shaped Storage V60 Coffee Filter Paper Holder
Coffee Filter Holder Coffee Paper Storage Rack Filter Paper Container Stand
Filter Paper Holder,Stainless Steel Filter Paper Holder,V60 Filter Paper Stand,wood filter paper storage stand
Jiangmen Chang Kun Industrial Co., Ltd. , https://www.changkun-houseware.com
