The unevenness of the surface of the printing plate and the surface adsorption directly affect the wettability of the printing plate. According to the actual printing conditions, improving and protecting the wettability of the printing plate is also an important step to improve the printing quality, which is particularly important for lithographic printing.
1. Coarse surface wetting. Assuming that the ratio of the real area to the smooth area of ​​the roughened surface is R', apparently the larger R' is, the more uneven the surface is, and R' is called the roughness coefficient. If the wetting equation is applied to a roughened surface system, the roughness coefficient correction should be added.
R'(γSG-γSL) = γLGcosθ' (1-19)
Exchange (1-19)
Cosθ′=R′(γSG-γSL)/γLG=R′cosθ (1-19)
then
R'=cosθ'/cosθ (1-20)
In the expression (1-20), θ′ is the contact angle on the roughened surface, and θ is the contact angle on the smooth surface. Because R'>1, so
The absolute value of cosine ? of the roughened surface is larger than the absolute value of cos? of the smooth surface. This means that when θ<90°, solid
The rougher the surface, the better the wettability; when θ>90°, the rougher the solid surface, the worse the surface wettability. That is, as the surface roughness increases, the easily wetted surface becomes more wettable, while the hard wetted surface becomes more difficult to wet. This is the use of mechanical or electrochemical methods, the formation of sand on the surface of the metal lithographic surface, the surface roughening, thereby improving the wettability of the plate surface, is conducive to the formation of a stable hydrophilic and oleophilic film.
However, the two metals, aluminum and zinc, have relatively low mechanical strength, and in order to increase their mechanical strength, a small amount of other metals are often incorporated. For example, the purity of zinc plate is about 90%, and the remaining 10% is lead, cadmium, iron, copper and other metals. The purity of the aluminum plate is about 99%, and the remaining 1% is copper, magnesium, manganese and other metals. Since a variety of metals exist in the zinc plate and the aluminum plate, when the surfaces of the zinc plate and the aluminum plate are covered with the electrolyte solution and the water film, the primary battery is formed. Taking a zinc plate as an example, the standard electrode potential E° of zinc is -0.76 V, and the standard electrode potential E of copper is +34 V. The standard electrode potentials of the two metals differ greatly. If the zinc plate after grinding has been exposed to moist air for a long period of time, the water film covers the surface of the zinc plate, which forms a primary battery. The anode (negative) of the primary battery is zinc, and the cathode (positive) of the primary battery is copper, as shown in Figure 1-19. In a primary battery composed of zinc, copper, and water, zinc enters water in the form of zinc ions, excess electrons move toward copper, hydrogen ions combine with electrons on copper to generate hydrogen gas, zinc ions in the water film and Hydroxide ions combine to form zinc hydroxide. The entire electrochemical reaction is:
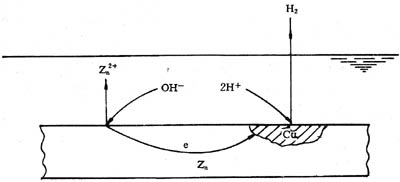
Figure 1-19 Electrochemical corrosion of a lithographic substrate
Anode (Zinc) Zn-2e=Zn2+
Zn2++2OH=Zn(OH)2
Cathode (copper) 2H++2e=H2
The overall reaction equation is:
Zn+2H2O=Zn(OH)2+H2↑
Zinc hydroxide is very unstable, zinc oxide produced after dehydration attached to the zinc plate.
As a result of galvanic corrosion, the grain on the plate is destroyed, and the wettability of the plate decreases. Therefore, the formation of sand aluminum or zinc plate should be immediately pre-coated photosensitive treatment. Due to the limited conditions, when the photosensitive film cannot be coated in time, the aluminum plate and zinc plate that forms the sand should be placed in a dry and ventilated place in order to avoid galvanic corrosion.
In addition, during the printing process, the plate will be worn due to the friction of various rollers. In order to maintain the good wettability of the printing plate, the wear of the printing plate caused by various factors should be minimized in the printing.
